いまさらながらの MCP サーバ お試しです。
で、MCPとは?公式の説明を引用します。
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open-source standard for connecting AI applications to external systems.
Using MCP, AI applications like Claude or ChatGPT can connect to data sources (e.g. local files, databases), tools (e.g. search engines, calculators) and workflows (e.g. specialized prompts)—enabling them to access key information and perform tasks.
Think of MCP like a USB-C port for AI applications. Just as USB-C provides a standardized way to connect electronic devices, MCP provides a standardized way to connect AI applications to external systems.
具体例で説明すると…
あなたが AI クライアント(例:ChatGPT)を使っているとします。質問をすると回答が返ってきますよね。この回答は ChatGPT が学習済みのデータに基づいて行われます。ここで ChatGPT にあなたの Google カレンダーの内容に基づいて今日の予定を教えてほしいと質問したとします。ChatGPT はあなたの Google カレンダーの内容は学習していないので、答えることができません。では、ChatGPT があなたの Google カレンダーにアクセスできるようにしたらどうでしょう?ChatGPT はあなたの Google カレンダーにアクセスして、今日の予定を教えてくれるようになります。
このとき、ChatGPT と Google カレンダーをつなぐ役割を果たすのが MCP です。MCP は AI クライアントと外部のデータソースやツールをつなぐためのプロトコルです。
そして MCP のプロトコルを使って AI クライアントと外部ソースをつなぐためのサーバを MCP サーバと呼びます。
[ChatGPT] --- MCP ---> [MCP サーバ] --- API ---> [Google カレンダー]
では、MCP サーバを実装してみましょう。そして AI クライアントとして Claude Desktop を使って、MCP サーバを通じて予定を回答してもらいます。
MCP サーバの実装 #
デスクトップに main.js というファイルを作成して、以下のコードを貼り付けます。
このコードは、Claude Desktop から「今日の予定を教えて」といったリクエストがあったときに、あらかじめ用意した今日の予定を返すだけのシンプルな MCP サーバです。
(このコードは Codex がつくってくれました)
/*
Minimal MCP server sample
*/
const TODAY_SCHEDULE = [
"今日の予定",
"- 09:00 ランニング",
"- 10:00 カフェで読書",
"- 12:00 お昼ご飯",
"- 14:00 映画鑑賞",
"- 18:00 友達とディナー",
"- 21:00 夜景を見に行く",
].join("\n");
main();
async function main() {
const parse = createFlexibleStdioParser(handleRequest);
process.stdin.on("data", parse);
process.stdin.resume();
}
function sendResult(id, result) {
const json = JSON.stringify({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id,
result,
});
process.stdout.write(`${json}\n`);
}
function sendError(id, code, message) {
const json = JSON.stringify({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: id,
error: { code, message },
});
process.stdout.write(`${json}\n`);
}
function handleRequest(message) {
if (!("id" in message)) {
// Ignore notifications such as notifications/initialized.
return;
}
const { id, method, params } = message;
switch (method) {
case "initialize": {
sendResult(id, {
protocolVersion: "2025-11-25",
capabilities: {
tools: {
listChanged: false,
},
},
serverInfo: {
name: "minimal-today-schedule",
version: "0.1.0",
},
});
return;
}
case "tools/list": {
sendResult(id, {
tools: [
{
name: "get_today_schedule",
description: "今日の予定を返します",
inputSchema: {
type: "object",
properties: {},
additionalProperties: false,
},
},
],
});
return;
}
case "tools/call": {
if (params?.name === "get_today_schedule") {
sendResult(id, {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: TODAY_SCHEDULE,
},
],
});
}
}
}
}
function createFlexibleStdioParser(onMessage) {
let byteBuffer = Buffer.alloc(0);
let mode = null;
function emitJson(text) {
const trimmed = text.trim();
if (!trimmed) {
return;
}
onMessage(JSON.parse(trimmed));
}
return (chunk) => {
byteBuffer = Buffer.concat([byteBuffer, chunk]);
while (true) {
if (!mode) {
const probe = byteBuffer.toString("utf8");
if (/^Content-Length:/i.test(probe)) {
mode = "content-length";
} else if (byteBuffer.includes(0)) {
mode = "nul";
} else if (probe.includes("\n")) {
mode = "newline";
} else {
return;
}
}
if (mode === "content-length") {
let headerEnd = byteBuffer.indexOf("\r\n\r\n");
let separatorLength = 4;
if (headerEnd === -1) {
headerEnd = byteBuffer.indexOf("\n\n");
separatorLength = 2;
}
if (headerEnd === -1) {
return;
}
const headerText = byteBuffer.slice(0, headerEnd).toString("utf8");
const headers = headerText.split(/\r?\n/);
let contentLength = null;
for (const line of headers) {
const match = /^Content-Length:\s*(\d+)$/i.exec(line.trim());
if (match) {
contentLength = Number(match[1]);
break;
}
}
if (!Number.isInteger(contentLength) || contentLength < 0) {
return;
}
const bodyStart = headerEnd + separatorLength;
const bodyEnd = bodyStart + contentLength;
if (byteBuffer.length < bodyEnd) {
return;
}
const body = byteBuffer.slice(bodyStart, bodyEnd).toString("utf8");
byteBuffer = byteBuffer.slice(bodyEnd);
emitJson(body);
continue;
}
if (mode === "nul") {
const nulIndex = byteBuffer.indexOf(0);
if (nulIndex === -1) {
return;
}
const frame = byteBuffer.slice(0, nulIndex).toString("utf8");
byteBuffer = byteBuffer.slice(nulIndex + 1);
emitJson(frame);
continue;
}
const text = byteBuffer.toString("utf8");
const newlineIndex = text.indexOf("\n");
if (newlineIndex === -1) {
return;
}
const line = text.slice(0, newlineIndex);
byteBuffer = Buffer.from(text.slice(newlineIndex + 1), "utf8");
emitJson(line);
}
};
}
Claude Desktop で MCP サーバを設定 #
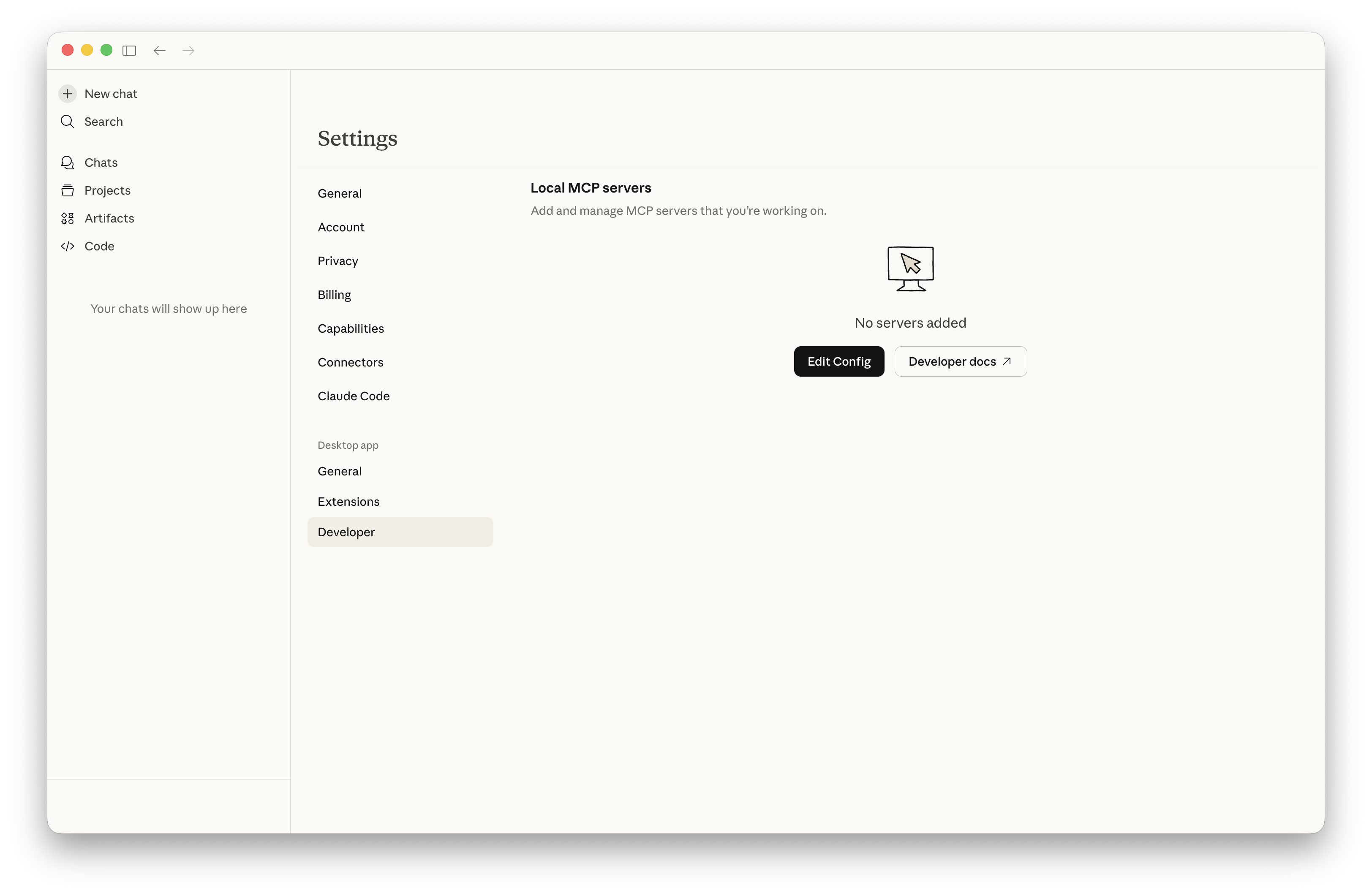
Claude Desktop を開いて Settings > Developer と進み Edit Config を押します。
すると claude_desktop_config.json というファイルが開きます。
mcpServers の項目を編集(存在しなければ追加)して、先ほど作成した main.js を呼び出すように設定します。
commandには Node.js の実行パスを指定します。パスは Node.js のインストール方法によって異なりますが、パスがわからなければwhich nodeコマンドで確認できますargsには先ほど作成したmain.jsへの絶対パスを指定します。
{
"preferences": {
// ... 省略
},
"mcpServers": {
"my-mcp": {
"command": "/usr/local/bin/node",
"args": ["/Users/alice/Desktop/main.js"]
}
}
}
その後、Claude Desktop を再起動します。
そして再び設定ページを開くと、MCP サーバが追加されていることがわかります。
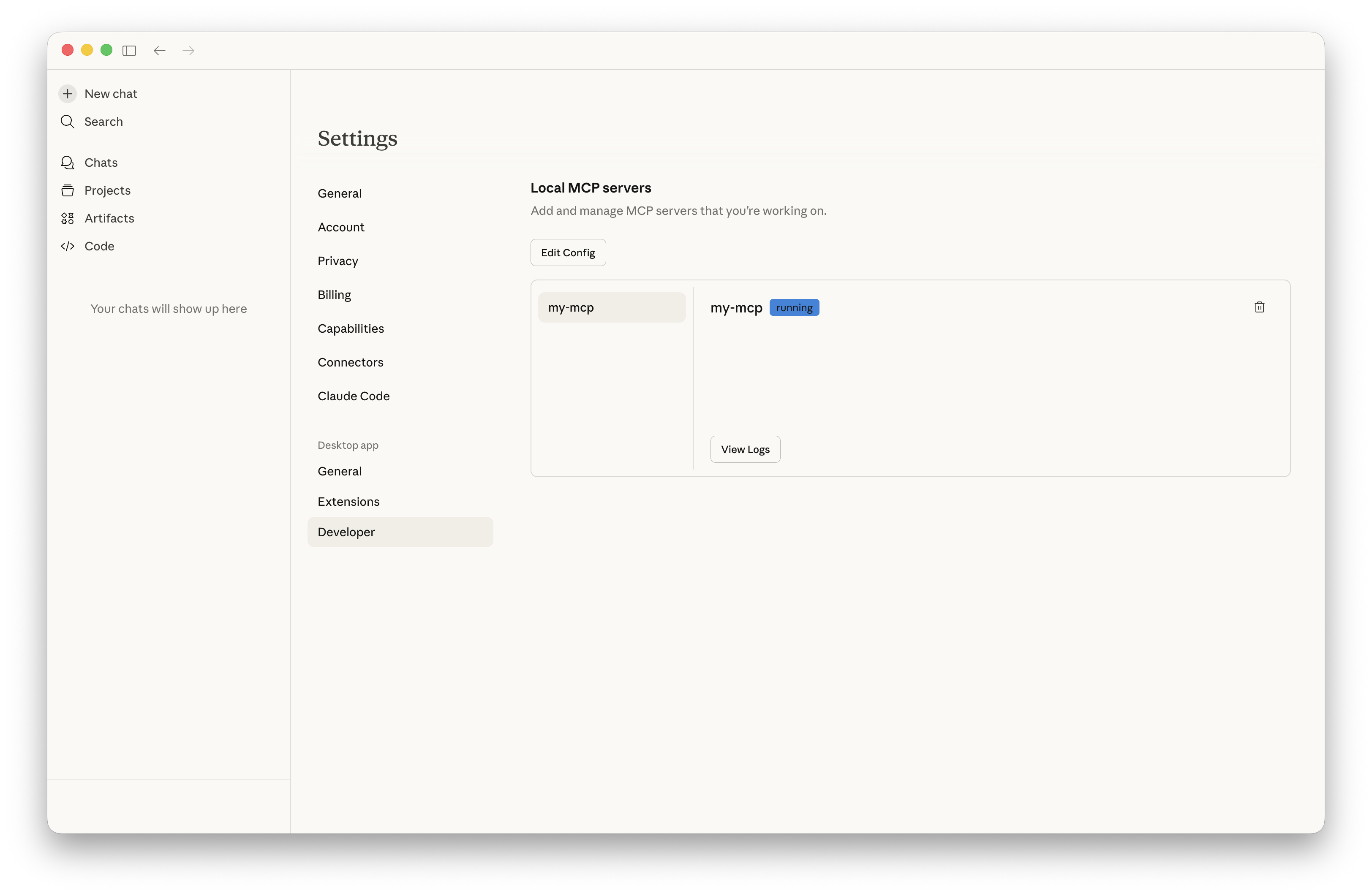
では、チャット画面に戻って、Claude に今日の予定を質問してみましょう。
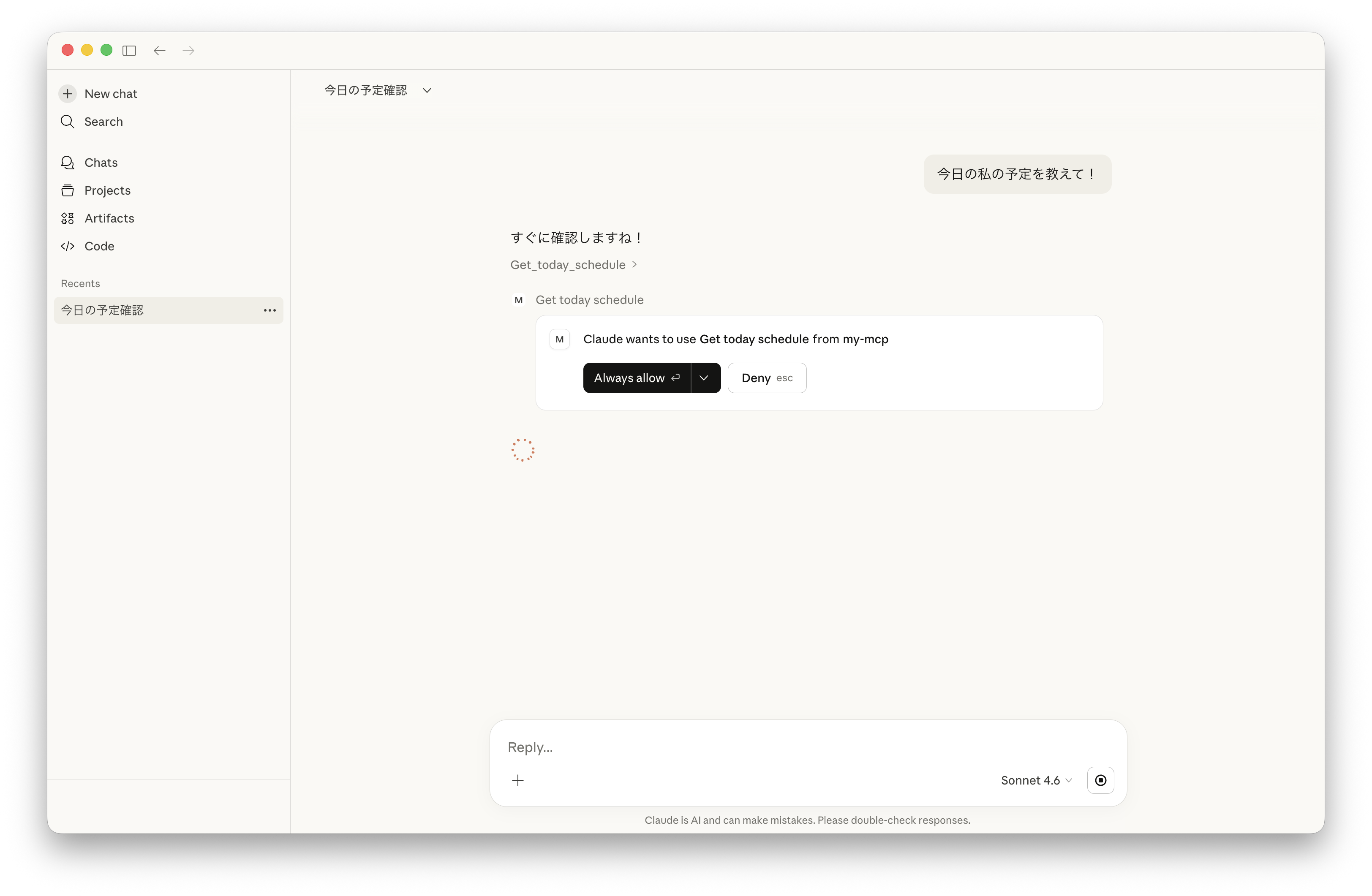
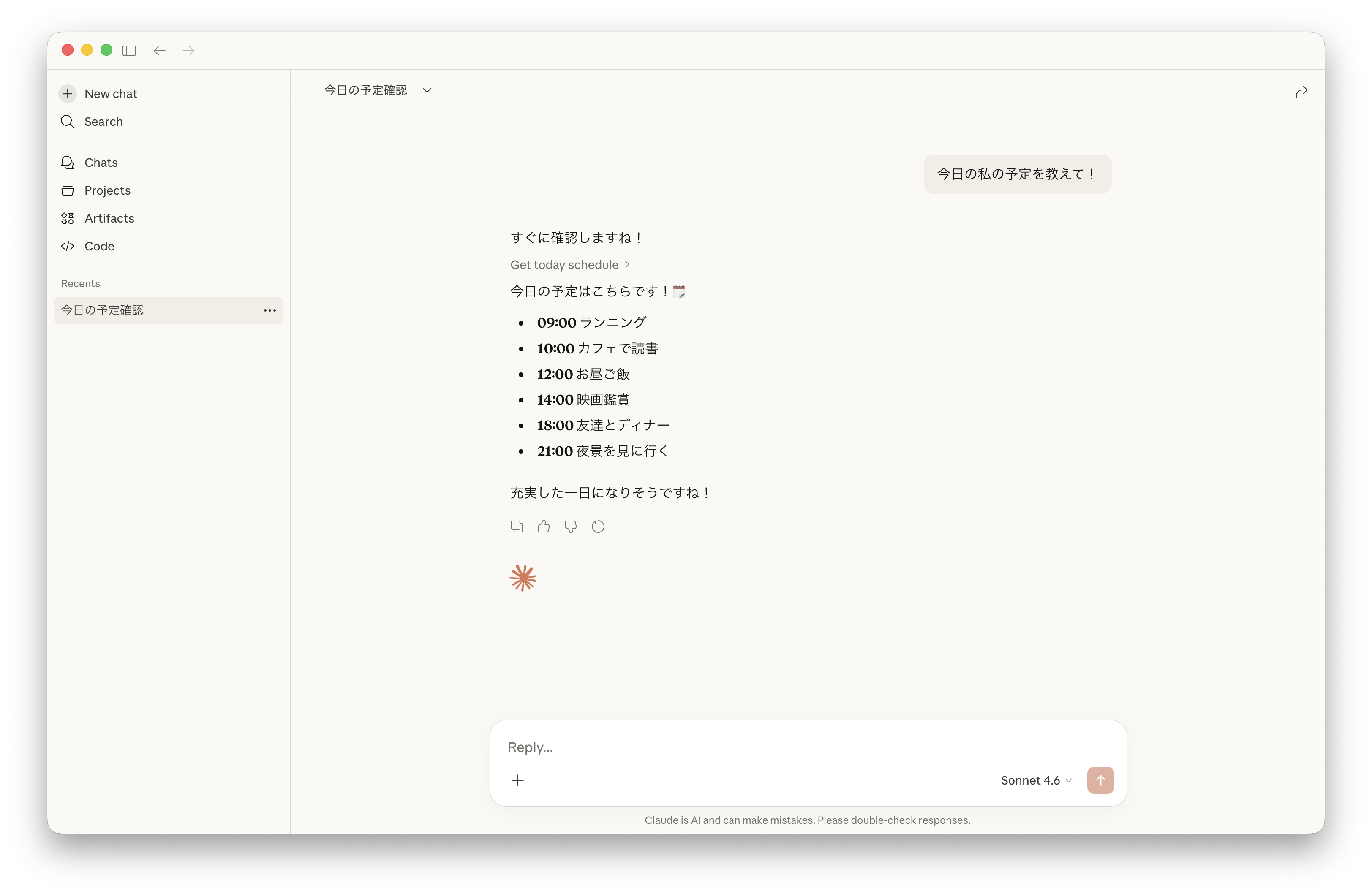
MCP サーバにアクセスしてよいかとの確認が出るので、許可します。
その後、今日の予定が返ってきました!MCP サーバを通じて情報が取得できていることがわかります。
おわり #
今回は MCP サーバのコードに予定をベタ書きしていましたが、MCP サーバから Google カレンダーの API を呼び出して予定を取得し、その予定を返すような実装にすれば、AI クライアントは MCP サーバを通じて Google カレンダーの予定を取得できるようになります。
こんな感じで、AI クライアントと外部リソースの仲介をするのが MCP サーバということですね。
今回は自作の MCP サーバを実装しましたが、すでに多くのサービスが MCP サーバを提供しています。以下は一例です。
- GitHub: https://github.com/github/github-mcp-server
- Figma: https://developers.figma.com/docs/figma-mcp-server/
- Notion: https://developers.notion.com/guides/mcp/mcp
このようにサービスが MCP サーバを提供している場合、ユーザは自分で MCP サーバを実装する必要はありません。
我々ユーザはその MCP サーバを呼び出すように AI クライアントを設定するだけで良く、今回の作業でいうと claude_desktop_config.json に GitHub や Figma、Notion の MCP サーバを呼び出す設定を追加するだけです。
こうして AI クライアントと様々な MCP サーバを連携することで、AI クライアントを通じて幅広い作業が可能となります。